Introduction
Dishwashers are a common household appliance, quietly performing the essential task of cleaning our dishes. Yet, despite their ubiquity, many people remain unfamiliar with the intricate science and technology that make these machines so effective. Understanding the mechanics and chemistry behind dishwashers can help consumers make informed decisions, optimize their use, and even troubleshoot common issues. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore how dishwashers work, diving deep into their components, the chemistry involved, and the latest technological advancements. Whether you’re curious about the history of dishwashers or want to know how to choose the best one for your needs, this article covers it all.
1. History of Dishwashers
The journey of the dishwasher begins in the 19th century, a time when manual labor was the primary method for cleaning dishes. The first recorded attempt to create a mechanical dishwasher was by Joel Houghton in 1850. His wooden device, operated by hand, featured a wheel that splashed water on dishes. Although primitive, it laid the foundation for future innovations. It wasn’t until Josephine Cochrane’s invention in 1886 that dishwashers began to resemble the modern machines we know today. Cochrane, frustrated with her servants chipping her fine china, designed a machine that used water pressure to clean dishes. Her design was patented and later showcased at the 1893 World’s Fair, earning her widespread recognition.
Throughout the 20th century, dishwashers evolved significantly. The introduction of electric-powered models in the 1920s marked a significant advancement. These machines were more efficient and reliable, making them more appealing to households. The post-World War II era saw a boom in dishwasher sales, particularly in the United States, as the economy flourished and consumer goods became more accessible. Manufacturers continued to innovate, adding features such as built-in drying elements and automatic detergent dispensers.
In the 1970s and 1980s, dishwashers became more energy-efficient, spurred by the oil crisis and growing environmental awareness. The introduction of energy labels helped consumers choose models that consumed less water and electricity. By the 1990s, dishwashers had become a standard appliance in many households around the world. Today, modern dishwashers boast a range of advanced features, from smart technology to eco-friendly settings, making them more efficient and user-friendly than ever before.

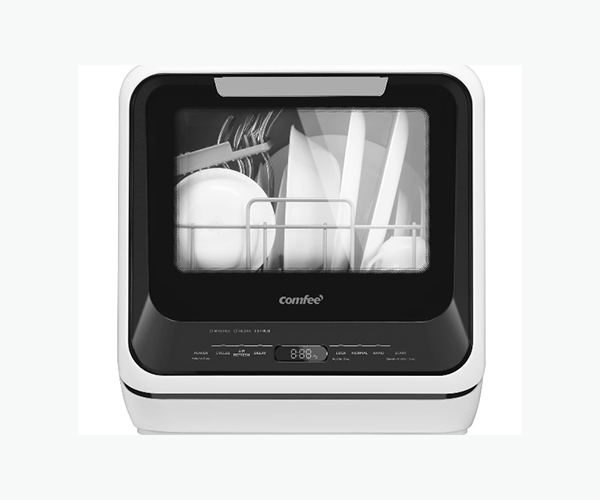
2. How Dishwashers Work: The Basics
At its core, a dishwasher is a complex machine designed to automate the process of cleaning dishes. Understanding how a dishwasher works involves looking at its key components and the typical cycle it follows.
Components Overview
A standard dishwasher consists of several essential parts, each playing a critical role in the cleaning process. The spray arms are perhaps the most visible component inside the machine. These rotating arms, usually located at the bottom and middle of the dishwasher, spray water onto the dishes. They are powered by a pump that circulates water throughout the machine. The detergent dispenser is another vital component, releasing detergent at the appropriate time during the wash cycle.
The filter system prevents food particles from clogging the spray arms and pump. Depending on the model, dishwashers may have a self-cleaning filter or a manual one that needs periodic cleaning. The heating element, usually found at the bottom of the dishwasher, is responsible for heating the water and assisting in the drying process. Lastly, the control panel allows users to select the desired wash cycle and settings.
The Washing Cycle
A dishwasher typically goes through several stages during a complete cycle, which can vary slightly depending on the model and selected settings. The pre-wash stage involves a quick rinse of the dishes to remove loose food particles. This step is crucial as it prevents large debris from clogging the machine’s internal components.
Next is the main wash stage, where hot water and detergent work together to break down food residues. The spray arms rotate, ensuring that water reaches all the dishes. During this stage, the water temperature can reach up to 140°F (60°C) or higher, depending on the selected cycle. The high temperature helps dissolve grease and sanitize the dishes.
Following the main wash, the machine enters the rinse stage. Here, fresh water is sprayed to remove detergent and any remaining food particles. Some dishwashers feature a rinse aid dispenser, which releases a chemical agent to prevent water spots and improve drying.
The final stage is drying, which can be achieved through various methods. Some models use a heating element to evaporate water, while others employ condensation drying, where cooler air is circulated inside the dishwasher to condense and drain away water. This latter method is more energy-efficient and gentler on dishes.
Types of Dishwashers
There are several types of dishwashers available, each suited to different needs and spaces. Built-in dishwashers are the most common, designed to be permanently installed under a kitchen counter. They offer various sizes and capacities, making them suitable for both small and large households.
Portable dishwashers are an excellent option for renters or those with limited kitchen space. These models can be wheeled to the sink when needed and stored away when not in use. They connect to the kitchen faucet and typically offer similar features to built-in models.
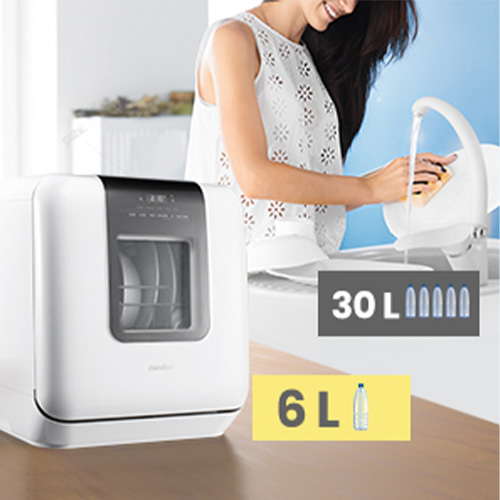
Countertop dishwashers are compact units that sit on the counter and are ideal for small apartments or RVs. They are less powerful than full-sized models but still offer a convenient solution for light dishwashing tasks.
Each type of dishwasher has its pros and cons, and the best choice depends on the user’s specific needs and circumstances. For example, a built-in model may offer more advanced features and greater capacity, while a portable or countertop model provides flexibility and space-saving benefits.
3. The Chemistry of Cleaning
The effectiveness of a dishwasher largely depends on the chemistry of the cleaning agents used and the interaction of these agents with water and food residues. Understanding these chemical processes can help users choose the right detergents and optimize their dishwasher’s performance.
Role of Detergents
Dishwasher detergents are specially formulated to tackle a wide range of food residues, from greasy oils to stubborn baked-on messes. These detergents typically contain a mix of enzymes, surfactants, and bleaches. Enzymes are biological molecules that break down proteins and starches into smaller, water-soluble molecules, making it easier for the detergent to wash them away. Common enzymes found in dishwasher detergents include proteases (for breaking down proteins) and amylases (for breaking down starches).
Surfactants are another crucial component, working to lower the surface tension of water. This allows water to spread more easily and reach all surfaces of the dishes, ensuring thorough cleaning. Surfactants also help lift and suspend dirt particles, preventing them from redepositing on the dishes. Bleaches, particularly oxygen-based bleaches, help remove stubborn stains and sanitize the dishes by killing bacteria and other microorganisms.
The choice of detergent can significantly impact the dishwasher’s cleaning performance. Powder detergents, gel detergents, and detergent tablets all have their unique properties and advantages. Tablets, for example, are pre-measured and convenient, ensuring the right amount of detergent is used for each load. Gels dissolve quickly and can be useful for short cycles, while powders are often more cost-effective.
Water Temperature
Water temperature plays a vital role in the dishwasher’s cleaning process. Hot water is more effective at dissolving grease and breaking down food particles. Most dishwashers are designed to heat water to a temperature of around 140°F (60°C), which is optimal for activating enzymes in the detergent and killing harmful bacteria.
In some cases, users may wonder if their dishwasher can clean effectively with cooler water. While lower temperatures can save energy, they may not provide the same level of cleaning power. However, some modern dishwashers come with advanced sensors and algorithms that can adjust the water temperature based on the load’s soil level and the selected cycle, providing an efficient balance between energy use and cleaning effectiveness.
pH Levels
The pH level of the water-detergent mixture also affects cleaning performance. Detergents are generally alkaline, with a pH level above 7. This alkalinity helps break down fats and oils, making them easier to wash away. However, excessively high pH levels can be harsh on delicate items like glassware and fine china. To mitigate this, many detergents include ingredients that help maintain a balanced pH, ensuring effective cleaning without damaging the dishes.
Water Softening
Hard water, which contains high levels of calcium and magnesium, can interfere with the cleaning process. These minerals can react with detergent ingredients, reducing their effectiveness and leading to the formation of unsightly white spots on dishes. To combat this, many dishwashers come equipped with a built-in water softener. This device uses salt to remove calcium and magnesium ions from the water, preventing mineral buildup and improving detergent performance.
In regions with very hard water, it may be necessary to use a water softening agent in addition to regular detergent. These agents work by binding to the minerals in hard water, preventing them from interfering with the cleaning process. This can help improve the dishwasher’s efficiency and prolong its lifespan.
Understanding the chemistry behind dishwasher cleaning can help users optimize their dishwashing routines and achieve better results. By choosing the right detergent, maintaining the appropriate water temperature, and managing water hardness, users can ensure their dishes come out sparkling clean every time.

4. Mechanical Action and Design
The mechanical design of a dishwasher is a crucial aspect that determines its cleaning efficiency and overall performance. From the spray arms to the filters, each component is designed to work in harmony, ensuring thorough cleaning while protecting delicate items. Let’s delve into the key mechanical elements and design features that contribute to a dishwasher’s cleaning power.
Spray Arms and Jets
The spray arms are the heart of the dishwasher’s cleaning mechanism. Typically, a dishwasher has two or three spray arms—one at the bottom, one in the middle, and sometimes one at the top. These arms are equipped with multiple jets that spray water at high pressure. The force of the water, combined with the movement of the spray arms, ensures that water reaches all surfaces of the dishes.
The design and placement of the jets are carefully engineered to create optimal spray patterns. This ensures that even hard-to-reach areas, such as the insides of glasses or the undersides of bowls, are thoroughly cleaned. Some advanced dishwashers feature variable-pressure jets, which can adjust the water pressure based on the type of load and the selected cycle. This helps provide a more customized cleaning experience, with gentle pressure for delicate items and stronger jets for heavily soiled dishes.
Filter Systems
A good filter system is essential for maintaining water cleanliness and preventing clogs. Dishwashers typically use either a manual or a self-cleaning filter. Manual filters need to be removed and cleaned periodically, usually located at the bottom of the dishwasher. These filters trap food particles and debris, preventing them from recirculating in the wash water.
Self-cleaning filters, on the other hand, use a grinder or a mesh to break down and flush away food particles. While more convenient, they can be noisier and are generally found in older models. Regardless of the type, a well-maintained filter is crucial for ensuring the dishwasher operates efficiently and prevents unpleasant odors.
Drying Mechanisms
Once the washing and rinsing are complete, the next step is drying the dishes. There are several methods dishwashers use to achieve this, with the most common being heat drying and condensation drying.
Heat drying involves a heating element that warms the air inside the dishwasher, evaporating the water from the dishes. This method is quick and effective but can consume a significant amount of energy. It can also be harsh on certain materials, such as plastics, which may warp under high temperatures.
Condensation drying, also known as air-dry, is a more energy-efficient method. In this process, cooler air is circulated inside the dishwasher, causing the water to condense on the walls and drain away. This method is gentler on dishes and is often used in conjunction with rinse aids, which help prevent water spots by encouraging water to sheet off the dishes.
Some modern dishwashers also offer a fan-assisted drying option. This feature uses a fan to circulate air, speeding up the drying process and improving overall efficiency. Additionally, some models incorporate zeolite minerals, which absorb moisture and release heat, providing a natural and energy-efficient drying method.
Understanding the mechanical aspects and design features of a dishwasher can help users optimize their cleaning routines and extend the lifespan of their appliances. By paying attention to the condition of the spray arms, filters, and drying mechanisms, users can ensure their dishwasher continues to perform at its best.
5. Innovations in Dishwasher Technology
The world of dishwashing has seen significant technological advancements over the years, transforming these appliances into highly efficient and intelligent machines. Today’s dishwashers are packed with features designed to enhance performance, reduce energy consumption, and offer greater convenience. Let’s explore some of the most notable innovations in dishwasher technology.
Smart Dishwashers
In the era of smart homes, dishwashers have not been left behind. Smart dishwashers come equipped with Wi-Fi connectivity, allowing users to control and monitor the appliance remotely via smartphone apps. This connectivity enables several convenient features, such as starting or stopping a wash cycle, adjusting settings, and receiving notifications about the cycle’s progress or any issues that may arise.
Some smart dishwashers also offer integration with virtual assistants like Amazon Alexa or Google Assistant, allowing users to control the appliance using voice commands. Additionally, smart diagnostics features can identify and troubleshoot problems, potentially saving users time and money on service calls. These advanced capabilities make smart dishwashers a popular choice for tech-savvy consumers looking for a seamless and integrated home experience.
Eco-Friendly Technologies
As environmental concerns grow, manufacturers have developed eco-friendly dishwasher technologies to minimize water and energy usage. Energy-efficient models often come with energy-saving modes or eco-cycles, which use less water and operate at lower temperatures. These cycles may take longer to complete, but they significantly reduce the appliance’s environmental footprint.
Another eco-friendly innovation is the use of sensor technology. Advanced sensors can detect the soil level on dishes and adjust the water pressure, temperature, and cycle duration accordingly. This not only ensures optimal cleaning but also conserves resources by using only the necessary amount of water and energy.
Water recycling systems are another exciting development. Some high-end dishwashers can filter and reuse the water from the rinse cycle for the next pre-wash, further reducing water consumption. Additionally, features like half-load options allow users to run the dishwasher with fewer dishes, making it more efficient for smaller households.
Noise Reduction
In the past, dishwashers were often loud, disruptive appliances. However, modern dishwashers have made significant strides in noise reduction. Manufacturers have incorporated quieter motors, improved insulation, and innovative designs to minimize noise levels. Some dishwashers operate as quietly as 40 decibels, roughly the sound level of a quiet library.
Inverter motors, used in some of the latest models, are particularly effective in reducing noise. These motors adjust their speed according to the load, making them quieter and more energy-efficient. Additionally, features like delayed start options allow users to run the dishwasher at night or during off-peak hours, minimizing any disruption.
Understanding these innovations can help consumers choose a dishwasher that fits their lifestyle and values. Whether prioritizing smart features, eco-friendliness, or quiet operation, there is a wide range of options available to meet various needs and preferences.
6. Common Myths and Misconceptions
Despite their widespread use, dishwashers are often subject to myths and misconceptions that can lead to inefficient use or even damage to the appliance. Let’s debunk some of the most common myths and clarify the truths behind them.
Pre-Rinsing Necessity
One of the most pervasive myths is that dishes need to be pre-rinsed before being placed in the dishwasher. While it may seem logical to remove food residues before washing, modern dishwashers are designed to handle soiled dishes. In fact, pre-rinsing can be counterproductive, as it reduces the dishwasher’s efficiency. The detergent needs something to latch onto, and pre-rinsing can make it harder for the detergent to clean effectively.
Additionally, pre-rinsing wastes water and energy. Most modern dishwashers come equipped with sensors that detect the soil level on dishes and adjust the cycle accordingly. Therefore, it’s more efficient to scrape off large food particles and let the dishwasher do the rest.
Energy Consumption
Another common misconception is that dishwashers consume more water and energy than hand washing. In reality, using a dishwasher can be more efficient, especially when washing full loads. Modern dishwashers are designed to use minimal water and operate at optimal temperatures, making them more energy-efficient than hand washing, which often involves running hot water continuously.
Moreover, many dishwashers offer energy-saving modes or eco-cycles that further reduce water and energy usage. By using these features and running the dishwasher with full loads, users can save both energy and money in the long run.
Effectiveness of Short Cycles
Some users believe that short cycles are less effective at cleaning dishes. While it’s true that short cycles use less water and energy, they can still be highly effective, depending on the soil level and the dishwasher’s technology. For lightly soiled dishes or small loads, short cycles can provide adequate cleaning while saving time and resources.
However, for heavily soiled dishes or large loads, a longer cycle with higher water temperatures and more detergent may be necessary for thorough cleaning. It’s essential to choose the appropriate cycle based on the load’s characteristics to achieve the best results.
Understanding these myths and the facts behind them can help users make better use of their dishwashers, ensuring efficient cleaning and prolonging the appliance’s lifespan.
7. Factors Affecting Dishwasher Performance
While dishwashers are designed to make life easier, several factors can influence their performance. By understanding these factors, users can optimize their dishwashing experience and achieve the best possible results.
Load Configuration
The way dishes are loaded into the dishwasher can significantly impact cleaning effectiveness. Overloading the dishwasher can prevent water and detergent from reaching all surfaces, leading to incomplete cleaning. On the other hand, underloading can waste water and energy. It’s essential to strike a balance and arrange dishes in a way that maximizes the machine’s efficiency.
For optimal results, place larger items like pots and pans on the bottom rack, with their open sides facing down or towards the center. Plates and bowls should be loaded with the dirty side facing the spray arms, while glasses and cups should be placed on the top rack, upside down. Utensils should be placed in the utensil basket, with handles facing down to avoid nesting and ensure thorough cleaning.
Type of Detergent
The choice of detergent can also affect the dishwasher’s performance. As mentioned earlier, detergents come in various forms, including powders, gels, and tablets. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages, and the best choice depends on the user’s preferences and the dishwasher’s specific requirements.
For instance, tablets are convenient and pre-measured, ensuring the right amount of detergent for each load. Gels dissolve quickly and can be ideal for short cycles, while powders are versatile and often more economical. It’s essential to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations and avoid using regular dish soap, as it can create excessive suds and damage the machine.
Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance is crucial for keeping the dishwasher in good working condition. This includes cleaning the filters, spray arms, and interior surfaces to prevent the buildup of food particles and mineral deposits. It’s also essential to check the detergent dispenser for clogs and ensure that the spray arms are free from obstructions.
Periodically running a cleaning cycle with a dishwasher cleaner can help remove grease and limescale, ensuring optimal performance. Additionally, inspecting the door seals and hinges for wear and tear can prevent leaks and other issues.
By paying attention to these factors and following proper maintenance practices, users can ensure their dishwasher operates efficiently and continues to provide excellent cleaning results.
8. Environmental and Health Considerations
While dishwashers are highly convenient and efficient, it’s essential to consider their environmental impact and potential health implications. Understanding these aspects can help users make more informed choices and adopt practices that align with their values.
Chemical Residue
One concern with dishwashers is the potential for chemical residue left on dishes after the cleaning process. Detergents and rinse aids contain various chemicals, including surfactants, enzymes, and bleaches, which can sometimes remain on dishes if not properly rinsed. While most dishwasher-safe products are designed to minimize residue, sensitive individuals may still experience reactions.
To reduce chemical residue, users can opt for natural or eco-friendly detergents free from harsh chemicals. These products typically use plant-based ingredients and are biodegradable, making them a safer choice for both health and the environment. Additionally, ensuring the dishwasher is correctly loaded and selecting the appropriate cycle can help improve rinsing efficiency, reducing the likelihood of residue.
Water and Energy Use
The environmental impact of dishwashers largely depends on their water and energy consumption. While dishwashers are generally more water-efficient than hand washing, their environmental footprint can vary based on the model and usage habits. Energy-efficient dishwashers with high Energy Star ratings use less water and electricity, making them a more sustainable choice.
To minimize the environmental impact, users can follow several best practices:
- Run full loads to maximize efficiency and reduce the number of cycles needed.
- Use energy-saving settings or eco-cycles that consume less water and operate at lower temperatures.
- Avoid pre-rinsing, as modern dishwashers are designed to handle soiled dishes without this step.
- Turn off the heat-dry option and allow dishes to air dry instead, which can save energy.
By adopting these practices, users can reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to water conservation efforts.
Sustainability Tips
In addition to choosing energy-efficient models and eco-friendly detergents, users can further enhance the sustainability of their dishwashing routines. Regular maintenance ensures that the dishwasher operates efficiently, preventing unnecessary water and energy consumption. Replacing worn-out parts and addressing minor issues promptly can extend the appliance’s lifespan, reducing the need for replacement and minimizing waste.
Another consideration is the disposal of old dishwashers. When it’s time to replace a dishwasher, users should seek out recycling programs or proper disposal methods. Many manufacturers and retailers offer take-back programs that recycle old appliances, recovering valuable materials and reducing landfill waste.
By making conscious choices and adopting eco-friendly habits, users can enjoy the convenience of dishwashers while minimizing their environmental impact and promoting a healthier home.
9. Choosing the Right Dishwasher
Selecting the right dishwasher involves considering various factors, from budget and features to brand reputation and personal needs. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you make an informed decision.
Budget Considerations
Dishwashers come in a wide range of prices, from basic models to high-end units with advanced features. It’s essential to determine a budget before shopping, as this will narrow down the options and help you focus on models that meet your financial criteria. While it’s tempting to go for the cheapest option, investing in a more expensive model can save money in the long run through energy efficiency and durability.
Basic models typically range from $300 to $600, offering essential features and decent performance. Mid-range models, priced between $600 and $1,000, often include additional features such as adjustable racks, multiple wash cycles, and improved energy efficiency. High-end models, which can cost upwards of $1,000, may offer advanced features like smart connectivity, specialized cleaning zones, and ultra-quiet operation.
Features to Look For
When choosing a dishwasher, consider the features that align with your needs and lifestyle. Some key features to look for include:
- Capacity: Dishwashers come in various sizes, typically measured by the number of place settings they can accommodate. For larger households, a dishwasher with a capacity of 14-16 place settings is ideal, while smaller households may find a compact model sufficient.
- Wash Cycles: Different wash cycles cater to various needs, from heavy-duty cleaning for pots and pans to delicate cycles for glassware. Consider the types of dishes you frequently wash and choose a model with appropriate cycle options.
- Adjustable Racks: Racks that can be adjusted or removed provide flexibility for loading different types of dishes and larger items.
- Noise Level: If the dishwasher is located near living areas, a quiet model (below 45 decibels) can be a valuable feature, ensuring minimal disruption.
- Smart Features: Wi-Fi connectivity, remote control, and smart diagnostics are increasingly common in modern dishwashers. These features can enhance convenience and provide additional functionality, such as monitoring energy usage or receiving maintenance alerts.
- Energy Efficiency: Look for dishwashers with high Energy Star ratings, which indicate superior energy and water efficiency. These models often come with eco-friendly cycles that use less water and lower temperatures.
Brand Comparisons
The brand of a dishwasher can significantly influence its quality, durability, and performance. Some of the most reputable dishwasher brands include:
- Bosch: Known for its quiet operation and high build quality, Bosch offers a range of models with innovative features like CrystalDry technology and flexible third racks.
- Whirlpool: A reliable brand offering a variety of affordable and mid-range models. Whirlpool dishwashers are known for their easy-to-use features and solid performance.
- KitchenAid: Popular for its premium features and stylish designs, KitchenAid dishwashers often include advanced cleaning technologies and flexible loading options.
- Samsung: Samsung dishwashers are known for their smart features and sleek designs. They often offer features like Zone Booster for targeted cleaning and AutoRelease door for improved drying.
- Miele: A luxury brand offering high-end dishwashers with top-notch performance and durability. Miele models often feature innovative drying systems and specialized wash cycles.
When choosing a brand, consider factors such as warranty, customer service, and the availability of replacement parts. Reading reviews and seeking recommendations can also provide valuable insights into the reliability and performance of different models.
10. Future Trends in Dishwasher Technology
As technology continues to evolve, dishwashers are becoming smarter, more efficient, and increasingly integrated into the broader smart home ecosystem. Here are some of the most exciting future trends in dishwasher technology.
AI and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning are set to revolutionize the way dishwashers operate. Future models may include AI-powered sensors that can identify the type and soil level of dishes, automatically selecting the optimal cycle and settings. This could lead to more efficient cleaning, reduced water and energy usage, and even the ability to learn from user preferences over time.
Machine learning algorithms could also be used to predict maintenance needs, alerting users when it’s time to clean filters, refill rinse aid, or schedule a service appointment. This proactive approach could prevent issues before they arise, extending the appliance’s lifespan and improving overall performance.
Advanced Sensors
Future dishwashers are likely to feature more advanced sensors that can monitor various aspects of the cleaning process in real-time. For example, sensors could measure water cleanliness, adjusting the wash cycle duration and detergent levels as needed. This would ensure optimal cleaning results with minimal resource use.
Other sensors might detect the presence of specific items, such as plastics or delicate glassware, and adjust the water temperature and pressure accordingly. This level of precision could enhance the safety and efficiency of the dishwasher, making it more versatile and user-friendly.
Integration with Smart Homes
As part of the growing trend toward smart homes, future dishwashers will likely offer deeper integration with other smart devices and systems. This could include compatibility with smart home assistants like Amazon Alexa and Google Assistant, allowing users to control the dishwasher using voice commands.
Integration with smart home energy management systems could also enable dishwashers to operate during off-peak hours, reducing energy costs. Additionally, features like auto-replenish, which orders detergent and other consumables when running low, could become standard, further simplifying the user experience.
Conclusion
Dishwashers have come a long way from their humble beginnings, evolving into sophisticated appliances that offer convenience, efficiency, and advanced features. Understanding the science and technology behind how dishwashers work can help users make informed choices, optimize their appliance’s performance, and even troubleshoot common issues. From the chemistry of cleaning agents to the mechanical design and future trends, this comprehensive guide provides a deep dive into the world of dishwashers.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect dishwashers to become even more intelligent, efficient, and eco-friendly. Whether you’re in the market for a new dishwasher or simply curious about how they work, staying informed about the latest innovations and best practices can help you make the most of this indispensable kitchen appliance.
Additional Resources
For those interested in learning more about dishwashers and related topics, here are some additional resources:
- HowStuffWorks: In-depth articles on how dishwashers and other appliances work.
- Energy Star: Information on energy-efficient appliances and tips for reducing energy consumption.
- Consumer Reports: Reviews and ratings for a wide range of dishwasher models and brands.
- Environmental Working Group: Guides on choosing eco-friendly cleaning products.
FAQs
Q: Is it safe to wash non-dishwasher-safe items in the dishwasher?\
A: No, non-dishwasher-safe items can be damaged or cause harm to the dishwasher. Always check the manufacturer’s instructions before placing items in the dishwasher.
Q: How often should I clean my dishwasher’s filter?\
A: It depends on the model and frequency of use, but generally, the filter should be cleaned every few weeks to prevent clogs and maintain performance.
Q: Can I use regular dish soap in the dishwasher?\
A: No, regular dish soap creates excessive suds that can overflow and damage the dishwasher. Always use detergent specifically designed for dishwashers.
Q: What should I do if my dishwasher isn’t cleaning properly?\
A: Start by checking the filter, spray arms, and detergent dispenser for clogs or obstructions. If the problem persists, consult the user manual or contact a professional for assistance.
By following these guidelines and staying informed, you can ensure that your dishwasher operates efficiently and continues to provide excellent cleaning results for years to come.












