Dishwashers have become an essential appliance in modern kitchens, offering a convenient and efficient method for cleaning dishes. Whether you’re new to using dishwashers or simply curious about their operation, this guide will help you understand the intricacies of these machines. We’ll explore everything from the fundamental components to the advanced features that enhance their functionality. Additionally, we’ll explain how dishwashers work, covering the entire process from loading dishes to the final drying cycle, ensuring you have a comprehensive understanding of this indispensable kitchen appliance.
1. The Basics of Dishwashers
What is a Dishwasher?
A dishwasher is an electrical appliance designed to clean and sanitize dishes, utensils, and other kitchenware. It automates the labor-intensive process of washing dishes by using water, detergent, and mechanical action. The primary purpose of a dishwasher is to save time and water while ensuring that dishes are thoroughly cleaned and sanitized.
Dishwashers have evolved significantly since their inception. The first mechanical dishwasher was invented in the 1850s, but it wasn’t until the 20th century that they became a common household appliance. Today’s dishwashers are highly advanced, offering a range of features that cater to various needs and preferences.
Types of Dishwashers
There are several types of dishwashers available in the market, each catering to different household needs. Understanding the types can help you choose the right one for your kitchen. Here are the most common types:
Built-in Dishwashers
Built-in dishwashers are the most common type, designed to be installed permanently under a kitchen counter. They are connected to the home’s plumbing system and typically offer a large capacity. Built-in models are popular because they seamlessly blend into kitchen cabinetry, providing a clean and cohesive look.
Portable Dishwashers
Portable dishwashers are freestanding units that can be moved around. They are ideal for smaller kitchens or apartments where permanent installation is not possible. These dishwashers can be connected to the kitchen faucet when in use and stored away when not needed. While they may not offer as much capacity as built-in models, they are a practical solution for those who need flexibility.
Drawer Dishwashers
Drawer dishwashers consist of two or more drawers that can be operated independently. They are convenient for small loads and allow for more flexible use of space. Drawer dishwashers are usually built into the cabinetry and are a popular choice for modern kitchens. They offer the advantage of running smaller loads without wasting water or energy.
Countertop Dishwashers
As the name suggests, countertop dishwashers are compact units that sit on the kitchen counter. They are perfect for small households or individuals who do not have a lot of dishes to wash. Countertop dishwashers are easy to install and use, making them a popular choice for small apartments or RVs.
Compact Dishwashers
Compact dishwashers are smaller versions of built-in models, typically 18 inches wide compared to the standard 24 inches. They are suitable for smaller kitchens or households with limited space. Despite their smaller size, compact dishwashers often offer many of the same features as full-sized models, including multiple wash cycles and energy-efficient settings.

Key Features of Modern Dishwashers
Modern dishwashers come equipped with a variety of features designed to enhance their efficiency and user-friendliness. Some of the key features include:
- Adjustable Racks and Shelves: These allow you to customize the interior layout to accommodate larger or oddly shaped items.
- Delay Start: This feature lets you schedule the dishwasher to start at a later time, which can be useful for taking advantage of off-peak electricity rates.
- Quiet Operation: Advances in insulation and motor design have made dishwashers quieter, allowing them to operate without disturbing household activities.
- Energy Efficiency: Many dishwashers are Energy Star certified, meaning they use less water and energy, making them environmentally friendly and cost-effective.
- Sensor Technology: Sensors can detect the soil level on dishes and adjust the wash cycle accordingly, ensuring optimal cleaning while conserving water and energy.
Understanding the basics and the different types of dishwashers sets the foundation for exploring how they work. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the key components and the step-by-step process of how dishwashers clean your dishes.
2. Key Components of a Dishwasher
The Main Parts
Dishwashers are composed of several essential components that work together to clean dishes efficiently. Understanding these parts can help you better grasp how dishwashers function and make troubleshooting easier. Here’s a breakdown of the key components:
The Control Panel
The control panel is the user interface of the dishwasher, where you can select different wash cycles, set timers, and adjust settings. It typically includes buttons, dials, or touch-sensitive areas, along with a display screen that shows the selected options and cycle status. The control panel allows you to customize the dishwasher’s operation based on the type and amount of dishes you need to clean.
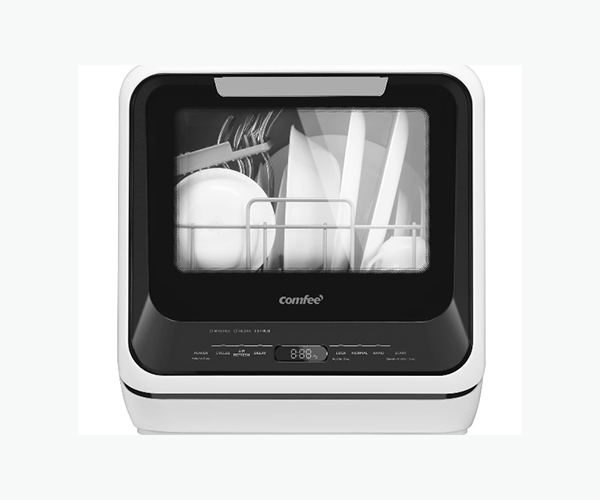
The Racks and Baskets
Inside the dishwasher, there are typically two or three racks designed to hold various types of dishes. The top rack is usually adjustable and can hold items like glasses, cups, and smaller plates. The bottom rack is designed for larger items like pots, pans, and dinner plates. Additionally, most dishwashers have a silverware basket or cutlery tray for utensils. The design and configuration of these racks can vary, with some models offering foldable tines and adjustable shelves to accommodate different dish sizes and shapes.
The Spray Arms
Spray arms are rotating components located at the bottom and, sometimes, the middle or top of the dishwasher. They are equipped with small nozzles that spray water onto the dishes. As water is pumped through the spray arms, they rotate and distribute water evenly throughout the dishwasher. The force and pattern of the water jets help remove food particles and stains from the dishes. Some dishwashers feature specialized spray arms with multiple nozzles or unique configurations for more efficient cleaning.
The Filter
The filter is an essential component that traps food particles and debris, preventing them from recirculating onto clean dishes. Most dishwashers have a filter located at the bottom of the tub. There are two main types of filters: self-cleaning and manual. Self-cleaning filters use a grinder or a mesh to break down food particles, which are then flushed away. Manual filters require regular cleaning to remove trapped debris. Proper filter maintenance is crucial for maintaining the dishwasher’s performance and preventing clogs.
The Heating Element
The heating element is responsible for heating the water to the appropriate temperature for cleaning and sanitizing dishes. It is usually located at the bottom of the dishwasher tub. The heating element also helps with the drying process by heating the air inside the dishwasher, which evaporates the water from the dishes. Some modern dishwashers use a condensation drying method instead, where the moisture condenses on cooler surfaces and drains away.
The Pump and Motor
The pump and motor work together to circulate water throughout the dishwasher. The pump draws water from the dishwasher’s tub and pushes it through the spray arms. It also handles draining the dirty water at the end of the wash cycle. The motor powers the pump and is a critical component for the dishwasher’s operation. Depending on the model, the motor may also control the rotation of the spray arms and other mechanical parts.
Additional Components
- Water Inlet Valve: Controls the flow of water into the dishwasher.
- Detergent Dispenser: Holds and releases detergent and rinse aid at the appropriate times during the cycle.
- Thermostat: Monitors the water temperature and ensures it reaches the required level for effective cleaning.
- Door Seal: A rubber gasket that prevents water from leaking out of the dishwasher.
Understanding these components is crucial for appreciating how dishwashers operate. Each part plays a specific role in ensuring that your dishes come out clean and dry. In the next section, we’ll explore the step-by-step process of how a dishwasher cleans dishes, from loading to drying.
3. How Dishwashers Work: Step-by-Step Process
1. Loading the Dishwasher
The first step in the dishwashing process is loading the dishwasher correctly. Proper loading ensures that all dishes are thoroughly cleaned and prevents damage to both the dishes and the dishwasher. Here’s a detailed look at how to load a dishwasher:
- Top Rack: The top rack is typically used for cups, glasses, small bowls, and light plastic items. Place items at an angle so that water can reach inside them and allow for better drainage. Avoid nesting bowls or stacking items, as this can obstruct water flow and prevent thorough cleaning.
- Bottom Rack: The bottom rack is designed for larger items like dinner plates, pots, pans, and casserole dishes. Place plates vertically, facing inward, and ensure that they do not block the spray arms. For pots and pans, position them upside down to allow water to reach inside. Large, flat items like baking sheets should be placed at the sides or back to avoid blocking the spray arms.
- Silverware Basket: Utensils should be placed in the silverware basket with the handles facing down. This arrangement allows the spray arms to reach the business end of the utensils, ensuring they are cleaned properly. However, if your dishwasher’s manual recommends handles up for safety or easier unloading, follow that guidance.
- Special Considerations: Some dishwashers have a third rack for cutlery and small items. This rack can be used for long utensils, lids, and other small items that might fall through the spaces in the other racks.
Proper loading not only ensures efficient cleaning but also protects your dishes and the dishwasher itself. Overloading or improper loading can lead to poor cleaning results and potential damage.
2. Adding Detergent
The next step involves adding detergent to the dishwasher. Detergent plays a crucial role in breaking down food particles and grease, ensuring that dishes come out clean and sparkling. Here’s what you need to know about adding detergent:
- Types of Detergents: There are three main types of dishwasher detergents: gel, powder, and pods. Gel detergents are liquid and easy to use, while powder detergents offer flexibility in dosage. Pods or tablets are pre-measured and convenient but can be more expensive.
- How Much to Use: The amount of detergent required depends on the dishwasher model, water hardness, and the number of dishes. It’s essential to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for the appropriate amount. Using too much detergent can lead to residue on dishes, while too little may result in inadequate cleaning.
- Where to Place Detergent: Most dishwashers have a detergent dispenser compartment located inside the door. This compartment typically has a cover that opens automatically during the wash cycle, releasing the detergent. Some models also have a secondary compartment for rinse aid, which helps with drying and preventing water spots.
3. Water Inlet and Heating
Once the dishwasher is loaded and detergent is added, the washing process begins with water intake. The water inlet valve opens, allowing water to enter the dishwasher. The amount of water used varies depending on the cycle selected, with some eco-friendly cycles using less water to conserve resources.
After the water enters the dishwasher, the heating element heats it to the desired temperature. The temperature of the water is crucial for effective cleaning and sanitizing. Most dishwashers heat water to temperatures between 120°F and 160°F (49°C to 71°C), depending on the cycle. Hot water helps dissolve grease and activate the detergent, ensuring that dishes are thoroughly cleaned.

4. Washing Cycle
The washing cycle is the heart of the dishwasher’s operation. During this phase, water is pumped through the spray arms, which rotate and distribute water evenly over the dishes. The detergent, dissolved in the hot water, breaks down food particles and stains.
- Pre-Wash Cycle: Some dishwashers have a pre-wash cycle, which rinses off loose food particles before the main wash. This step helps prevent debris from interfering with the cleaning process.
- Main Wash Cycle: The main wash cycle is where the detergent does most of the work. The water and detergent mixture is sprayed over the dishes with considerable force, ensuring thorough cleaning. The duration and intensity of this cycle can vary depending on the selected settings, such as heavy, normal, or eco.
- Rinse Cycle: After the main wash, the dishwasher drains the soapy water and refills with clean water for the rinse cycle. This cycle removes any remaining detergent and food particles from the dishes. Some dishwashers offer multiple rinse cycles for extra thoroughness.
- Final Rinse Cycle: The final rinse cycle may include the addition of rinse aid, which helps to prevent water spots and enhance drying. Rinse aid works by reducing the surface tension of water, allowing it to sheet off the dishes more effectively.
5. Drying Process
The final step in the dishwasher cycle is drying. There are several methods for drying dishes, and the method used can depend on the dishwasher model:
- Heated Drying: This method uses the heating element to warm the air inside the dishwasher, evaporating the water from the dishes. It is effective but consumes more energy.
- Condensation Drying: In this method, the hot dishes cool down, causing the moisture to condense on the cooler surfaces of the dishwasher walls. The water then drains away. This method is energy-efficient but may leave some moisture on plastic items.
- Fan-Assisted Drying: Some dishwashers use a fan to circulate air inside the dishwasher, speeding up the drying process. This method can be combined with either heated or condensation drying.
Each drying method has its advantages and trade-offs in terms of energy efficiency and drying performance. The choice of method can also depend on user preferences and the specific model of the dishwasher.
4. Advanced Features and Technologies
Sensor Technology
Modern dishwashers are equipped with advanced sensor technology that enhances their efficiency and effectiveness. Sensors can detect various factors during the washing process, allowing the dishwasher to adjust settings automatically for optimal performance. Here are some common types of sensors found in dishwashers:
- Soil Sensors: These sensors measure the amount of food particles and grease in the water. Based on the readings, the dishwasher can adjust the cycle length, water temperature, and detergent usage. This ensures that dishes are thoroughly cleaned without wasting water or energy.
- Water Hardness Sensors: Hard water can leave mineral deposits on dishes and reduce the effectiveness of detergent. Water hardness sensors detect the level of minerals in the water and can adjust the amount of detergent and rinse aid used. Some dishwashers can also alert users when a water softener needs to be added.
- Temperature Sensors: These sensors monitor the water temperature throughout the cycle, ensuring it reaches the required level for effective cleaning and sanitizing. If the water temperature is too low, the dishwasher can extend the cycle time to compensate.
Sensor technology not only improves cleaning efficiency but also enhances the overall user experience by simplifying operation and reducing the need for manual adjustments.
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is a crucial consideration for many homeowners when choosing a dishwasher. Energy-efficient dishwashers not only reduce environmental impact but also save on utility bills. Here are some features that contribute to energy efficiency:
- Energy Star Certification: Energy Star certified dishwashers meet strict energy efficiency guidelines set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). These models use less water and energy compared to non-certified models, making them a sustainable choice.
- Eco-Friendly Cycles: Many dishwashers offer eco-friendly cycles that use less water and lower temperatures. While these cycles may take longer, they significantly reduce energy and water consumption.
- Variable Speed Motors: Some modern dishwashers are equipped with variable speed motors that adjust the water pressure and spray intensity based on the load size and soil level. This feature ensures that the dishwasher uses only the necessary amount of water and energy for each load.
By choosing an energy-efficient dishwasher and using it properly, you can contribute to environmental conservation and enjoy long-term cost savings.
Smart Dishwashers
The rise of smart home technology has led to the development of smart dishwashers, which offer a range of advanced features for enhanced convenience and control. Here are some of the key features of smart dishwashers:
- Wi-Fi Connectivity: Smart dishwashers can be connected to your home Wi-Fi network, allowing you to control and monitor them remotely using a smartphone app. You can start or stop a cycle, check the status, and receive alerts when the cycle is complete.
- Voice Control: Many smart dishwashers are compatible with voice assistants like Amazon Alexa and Google Assistant. This allows you to control the dishwasher using voice commands, adding a layer of convenience.
- Smart Diagnostics: Some models come with smart diagnostics that can identify potential issues and provide troubleshooting tips. This feature can help you resolve minor problems without needing a technician.
- Maintenance Reminders: Smart dishwashers can track usage and alert you when it’s time to clean the filter, add rinse aid, or perform other maintenance tasks. This helps ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Smart dishwashers offer unparalleled convenience and can be a valuable addition to a smart home ecosystem. However, they may come with a higher price tag compared to traditional models.
5. Maintenance and Care Tips
Proper maintenance and care are essential for keeping your dishwasher in top condition and ensuring it performs efficiently. Regular upkeep can prevent common issues and extend the lifespan of the appliance. Here are some essential maintenance and care tips:
Regular Cleaning
- Clean the Filter: The dishwasher filter traps food particles and debris, preventing them from clogging the pump and spray arms. Depending on your dishwasher model, the filter may need to be cleaned weekly or monthly. Remove the filter and rinse it under warm water, scrubbing away any trapped debris.
- Wipe Down the Door and Seals: The door and door seals can accumulate grime and food particles. Wipe them down regularly with a damp cloth to prevent buildup and ensure a proper seal.
- Clean the Spray Arms: Over time, the spray arms can become clogged with mineral deposits or food particles. Remove the spray arms and clean them with a brush or toothpick to ensure the nozzles are clear.
- Run a Cleaning Cycle: Use a dishwasher cleaner or a mixture of vinegar and baking soda to run a cleaning cycle every few months. This helps remove mineral deposits, grease, and odors, keeping your dishwasher fresh and clean.
Preventing Common Issues
- Avoid Overloading: Overloading the dishwasher can obstruct the spray arms and prevent proper water circulation. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for loading dishes to ensure optimal cleaning.
- Rinse Dishes Before Loading: While modern dishwashers are designed to handle dirty dishes, rinsing off large food particles can prevent clogs and improve cleaning performance.
- Use the Right Detergent: Use dishwasher detergent specifically designed for automatic dishwashers. Avoid using regular dish soap, as it can create excessive suds and cause leaks.
- Check the Water Temperature: For effective cleaning, the water temperature should be at least 120°F (49°C). If your dishwasher isn’t heating the water properly, it may require servicing.
Handling Hard Water
Hard water can cause mineral deposits on dishes and reduce the efficiency of the dishwasher. Here’s how to deal with hard water:
- Use Rinse Aid: Rinse aid helps prevent water spots and mineral buildup. Add it to the dispenser as recommended by the manufacturer.
- Install a Water Softener: If you have consistently hard water, consider installing a water softener for your home. This can help reduce mineral deposits and improve the performance of your dishwasher and other appliances.
- Clean with Vinegar: Run a cleaning cycle with vinegar every few months to dissolve mineral deposits and keep the dishwasher clean.
By following these maintenance and care tips, you can keep your dishwasher running smoothly and avoid common issues. Proper maintenance not only ensures optimal performance but also extends the life of the appliance.
6. Troubleshooting Common Problems
Even with regular maintenance, dishwashers can sometimes encounter issues. Here are some common problems and their potential solutions:
Dishes Not Getting Clean
- Possible Causes: Overloading, improper loading, clogged spray arms, low water temperature, or using the wrong detergent can all result in dishes not getting clean.
- Solutions: Check the loading arrangement and avoid overcrowding. Clean the spray arms and filter. Ensure that the water temperature is at least 120°F (49°C) and use the recommended amount of detergent.
Dishwasher Not Draining
- Possible Causes: A clogged filter, blocked drain hose, or a malfunctioning drain pump can prevent the dishwasher from draining properly.
- Solutions: Clean the filter and check the drain hose for blockages. If the problem persists, the drain pump may need to be replaced or repaired.
Unusual Noises
- Possible Causes: Loose items inside the dishwasher, a faulty motor, or debris in the pump can cause unusual noises during operation.
- Solutions: Ensure that all items are securely placed and not touching the spray arms. If the noise persists, inspect the motor and pump for any issues.
Leaks and Water Spots
- Possible Causes: Leaks can result from a damaged door seal, overfilling, or using the wrong detergent. Water spots may be caused by hard water or insufficient rinse aid.
- Solutions: Check the door seal for damage and replace if necessary. Ensure that the dishwasher is not overloaded and use the recommended detergent. Add rinse aid to prevent water spots.
Dishwasher Won’t Start
- Possible Causes: A power issue, a faulty door latch, or a problem with the control panel can prevent the dishwasher from starting.
- Solutions: Check the power supply and ensure that the door is securely closed. If the control panel is unresponsive, it may need to be replaced.
While some issues can be resolved with simple troubleshooting, others may require professional repair. Always refer to the manufacturer’s manual for specific troubleshooting steps and contact a qualified technician if needed.
7. Choosing the Right Dishwasher for Your Needs
When selecting a dishwasher, it’s essential to consider various factors to ensure that it meets your specific needs and preferences. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you make an informed decision:
Factors to Consider
- Size and Capacity: Dishwashers come in different sizes and capacities. Consider the size of your household and the amount of dishwashing you typically do. Full-sized models are ideal for larger households, while compact models are suitable for smaller kitchens or couples.
- Noise Level: The noise level of a dishwasher is measured in decibels (dB). Lower decibel levels indicate quieter operation. If your kitchen is open to living areas, consider choosing a dishwasher with a low noise level for minimal disruption.
- Wash Cycles and Options: Look for dishwashers with a variety of wash cycles and options, such as heavy, normal, eco, and quick wash. Additional features like delayed start, sanitize, and half-load options can provide more flexibility.
- Energy Efficiency: Energy Star certified dishwashers are more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly. They use less water and energy, which can save you money on utility bills.
- Advanced Features: Consider additional features like adjustable racks, third racks, smart connectivity, and sensor technology. These features can enhance convenience and improve the overall cleaning performance.
Budget and Value
Dishwashers vary in price based on brand, features, and design. While it can be tempting to opt for a more affordable model, it’s essential to consider the long-term value and potential cost savings from energy efficiency and durability. Investing in a high-quality dishwasher with advanced features may offer better performance and reliability over time.
When comparing models, consider the warranty and customer support offered by the manufacturer. A good warranty can provide peace of mind and protect your investment.
8. Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Dishwashers play a significant role in conserving water and energy compared to hand washing. However, there are additional steps you can take to minimize the environmental impact of your dishwasher use:
Water and Energy Usage
- Efficient Water Use: Modern dishwashers use significantly less water than hand washing. On average, a dishwasher uses 3 to 5 gallons of water per cycle, compared to 20 gallons or more for hand washing.
- Energy Conservation: Choose energy-efficient cycles and run the dishwasher only when it’s full. Avoid using the heated drying option if possible, as air drying is more energy-efficient.
Eco-Friendly Detergents
Using eco-friendly detergents can reduce the environmental impact of your dishwasher. These detergents are biodegradable and free from harmful chemicals like phosphates, which can pollute water sources. Look for products labeled as environmentally friendly or green-certified.
Sustainable Practices
- Use Rinse Aid: Rinse aid helps improve drying efficiency and prevent water spots, reducing the need for additional cleaning or polishing.
- Proper Disposal: When replacing an old dishwasher, dispose of it properly. Many municipalities offer recycling programs for appliances, ensuring that valuable materials are recovered and reused.
- Maintain and Repair: Regular maintenance and timely repairs can extend the life of your dishwasher, reducing the need for replacements and minimizing waste.
By adopting these sustainable practices, you can enjoy the convenience of a dishwasher while minimizing its environmental impact.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How often should I clean my dishwasher?
It’s recommended to clean your dishwasher’s filter, spray arms, and interior every 1 to 3 months, depending on usage. Regular cleaning prevents buildup of food particles and grease, ensuring optimal performance and hygiene.
Can I wash plastic items in the dishwasher?
Yes, but it’s important to place plastic items on the top rack to avoid exposure to the heating element, which can cause melting or warping. Some dishwashers have a low heat or eco cycle specifically for plastic items.
What is the best detergent to use?
The best detergent depends on your dishwasher and personal preferences. Powder detergents offer flexibility in dosage, while pods are convenient and pre-measured. Gel detergents are easy to use but may not be as effective for heavy loads. Consider using a detergent with built-in rinse aid for better drying and spot prevention.
Is it safe to open the dishwasher mid-cycle?
Most dishwashers allow you to open the door mid-cycle, but it’s best to consult the user manual. Opening the door can interrupt the cycle and cause hot water to spill out. If you need to add an item, pause the cycle and wait for the spray arms to stop before opening the door.
Conclusion
Dishwashers are an essential appliance in modern kitchens, offering convenience, efficiency, and effective cleaning. Understanding how dishwashers work, from loading to drying, can help you choose the right model, maintain it properly, and troubleshoot common issues. With advanced features and energy-efficient designs, dishwashers continue to evolve, making them an eco-friendly and valuable addition to any home.
Whether you’re a first-time dishwasher user or looking to upgrade, this guide provides all the information you need to make an informed decision. Remember to consider your specific needs and preferences when selecting a dishwasher, and follow proper maintenance practices to ensure long-lasting performance.
For more tips and guides on household appliances, subscribe to our blog and join the conversation in the comments section. We’d love to hear your experiences and answer any questions you may have!












